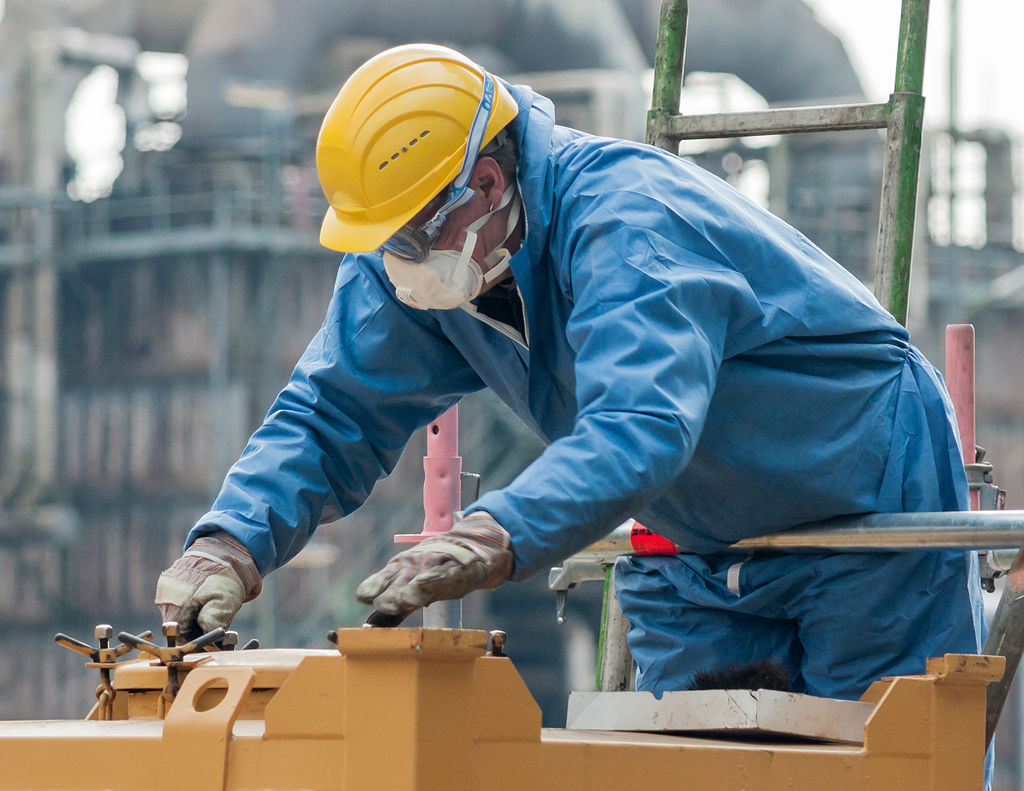
Keeping your crew safe on the job shows itself in a variety of ways, from the proper equipment training, providing water, and outfitting your team in proper personal protective equipment (PPE).
Cut resistant gloves, steel-toed boots and hard hats are a few of the most common pieces of PPE, but there are a few other crucial pieces of equipment that often get overlooked.
There are three types of PPE most often overlooked:
- Ear plugs
- Safety goggles
- Respiratory protection
OSHA law states that employers must provide and pay for personal protective equipment including “eye protection, protective hearing protection (earplugs, muffs), hard hats, and respirators.”
Ear Plugs
While a very small thing, ear plugs can play a huge impact on the safety of your construction crew. Exposure to loud noise can cause permanent hearing loss and there are an abundance of loud noises on a construction site.
Six of the loudest construction tasks and their dBA range:
- Manlift: 98.1 – 117.6 dBA
- Welding: 98.4 – 119.7 dBA
- Demolition: 99.3 – 112.1 dBA
- Grinding: 99.7 – 118.6 dBA
- Bulldozer: 100.2 – 112.5 dBA
- Chipping Concrete: 102.9 – 120.3 dBA
- Airsoft Red Poly Cord Ear Plugs
- Super-Soft Cordless Foam Ear Plugs
- Laser Lite Soft Foam Ear Plugs
- Soft Superfit Ear Plugs
Four of the loudest construction tools:
- Welding and Cutting Equipment: 94.9 – 122.8 dBA
- Hand Power Saw: 95.4 – 118.3 dBA
- Chop Saw: 97.2 – 114.0 dBA
- Screw Gun: 97.7 – 123.7 dBA
Damage to your hearing can only be prevented. Once the damage has occurred, it cannot be reversed. The dangerous aspect of hearing loss is that it happens slowly, after constant exposure, and the effects might be ignored or go unnoticed for months.
Your team should keep a sound level meter reader with the rest of their PPE gear. This tool allows you to measure the decibels when different tools and equipment are in use. Measuring the decibel levels will help direct you as to what type of ear plugs will be best. OSHA also recommends a few ways to limit exposure:
- Use prefabricated noise barriers
- Purchase quieter tools and equipment
- Limit hours worked in hazardous noise areas
Safety Goggles
Damage to your eye can take only a split second. Whether it’s a rouge nail or sawdust, there are 2,000 eye-related injuries every day, 90% of which could be avoided if proper eye protection was worn.
Eye injuries are most common during these activities:
- Welding
- Cutting
- Grinding
- Nailing
- Working with concrete or chemicals
- Masonry and carpentry work
Knowing which type of eye protection to buy for your crew depends on which activities they do most. When buying goggles for welding, you will want safety glasses with UV protection.
- Chemical Splash Safety Glasses
- Clean Lens Safety Glasses
- Anti-Fog Goggles with Face Shield
- Dark Lense Saftey Glasses
Three common types of eye protection goggles:
- General Safety Glasses: used for general work and protection from dust and other particles.
- Safety Goggles: used for high impact, chemical splashes and welding.
- Face Shields: used for high impact hazards such as harsh chemicals and bloodborne hazards.
Respiratory Protection
Any type of construction work will stir up dust, gases, and fumes of all kinds. Keeping these out of your lungs is important for your long-term health. You don’t often know what you will be digging into and it is important to keep your lungs protected from the start.
The health effects of breathing in unknown substances if often not known immediately and sometimes it can take years for symptoms to occur.
Common respiratory hazards in construction are:
- Solvent vapors: adhesives, paints, strippers, spray coatings, cleaning chemicals
- Lead dust
- Silica dust
- Isocyanate vapors: spray foam insulation, spray paints, coatings
When choosing a respirator, it needs to be certified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Employers and contractors are required by law to test respirator in the workplace to make sure the respirator will properly protect workers from the present hazards.
Three types of respirators:
- Air-purifying: used to clean the air of particles, gas and vapors.
- Filters: used to remove solids, or liquid aerosols.
- Cartridges: used to filter contaminants out of the air with cartridges that change colors to indicate when to change the filter.
- Particulate Respirator with Valve
- Mask Respirator
- Particulate Respirator
Selecting the Proper PPE
Many workers choose not to use these types of PPE because they are not available, they are not properly trained on the importance of their use, or the equipment does not properly fit.
No matter the excuse, as an employer it is your responsibility to make sure your team has access to proper PPE and knows the how and why. Many of the injuries caused can be avoided and hearing, eye, and respiratory injuries have some of the worst long term effects.
To make sure you are getting the proper equipment, pair up with a local PPE provider to do a worksite audit to determine the hazards and get recommendations on exactly what you and your team need.